China Roundup: Tencent’s new US gaming studio and WeChat’s new paywall
Hello and welcome back to TechCrunch’s China Roundup, a digest of recent events shaping the Chinese tech landscape and what they mean to people in the rest of the world.
The spotlight this week is back on Tencent, which has made some interesting moves in gaming and content publishing. There will be no roundup next week as China observes the Lunar New Year, but the battle only intensifies for the country’s internet giants, particularly short-video rivals Douyin (TikTok’s Chinese version) and Kuaishou, which will be vying for user time over the big annual holiday. We will surely cover that when we return.
‘Honor of Kings’ creator hiring for U.S. studio
Tencent’s storied gaming studio TiMi is looking to accelerate international expansion by tripling its headcount in the U.S. in 2020, the studio told TechCrunch this week, though it refused to reveal the exact size of its North American office. Eleven-year-old TiMi currently has a team working out of Los Angeles on global business and plans to grow it into a full development studio that “helps us understand Western players and gives us a stronger global perspective,” said the studio’s international business director Vincent Gao.
Gao borrowed the Chinese expression “riding the wind and breaking the wave” to characterize TiMi’s global strategy. The wind, he said, “refers to the ever-growing desire for quality by mobile gamers.” Breaking the wave, on the other hand, entails TiMi applying new development tools to building high-budget, high-quality AAA mobile games.
The studio is credited for producing one of the world’s most-played mobile games, Honor of Kings, a mobile multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) game, and taking it overseas under the title Arena of Valor. Although Arena of Valor didn’t quite take off in Western markets, it has done well in Southeast Asia in part thanks to Tencent’s publishing partnership with the region’s internet giant Garena.
Honor of Kings and a few other Tencent games have leveraged the massive WeChat and QQ messengers to acquire users. That raises the question of whether Tencent can replicate its success in overseas markets where its social apps are largely absent. But TiMi contended that these platforms are not essential to a game’s success. “TiMi didn’t succeed in China because of WeChat and QQ. It’s not hard to find examples of games that didn’t succeed even with [support from] WeChat and QQ.”

Call of Duty: Mobile is developed by Tencent and published by Activision Blizzard (Image: Call of Duty: Mobile via Twitter)
When it comes to making money, TiMi has from the outset been a strong proponent of game-as-a-service whereby it continues to pump out fresh content after the initial download. Gao believes the model will gain further traction in 2020 as it attracts old-school game developers, which were accustomed to pay-to-play, to follow suit.
All eyes are now on TiMi’s next big move, the mobile version of Activision Blizzard’s Call of Duty. Tencent, given its experience in China’s mobile-first market, appears well-suited to make the mobile transition for the well-loved console shooter. Developed by Tencent and published by Blizzard, in which Tencent owns a minority stake, in September, Call of Duty: Mobile had a spectacular start, recording more worldwide downloads in a single quarter than any mobile game except Pokémon GO, which saw its peak in Q3 2016, according to app analytics company Sensor Tower.
The pedigreed studio has in recent times faced more internal competition from its siblings inside Tencent, particularly the Lightspeed Quantum studio, which is behind the successful mobile version of PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds (PUBG). While Tencent actively fosters internal rivalry between departments, Gao stressed that TiMi has received abundant support from Tencent on the likes of publishing, business development and legal matters.
WeChat erects a paywall – with Apple tax
Ever since WeChat rolled out its content publishing function — a Facebook Page equivalent named the Official Account — back in 2012, articles posted through the social networking platform have been free to read. That’s finally changing.
This week, WeChat announced that it began allowing a selected group of authors to put their articles behind a paywall in a trial period. The launch is significant not only because it can inspire creators by helping them eke out additional revenues, but it’s also a reminder of WeChat’s occasionally fraught relationship with Apple.
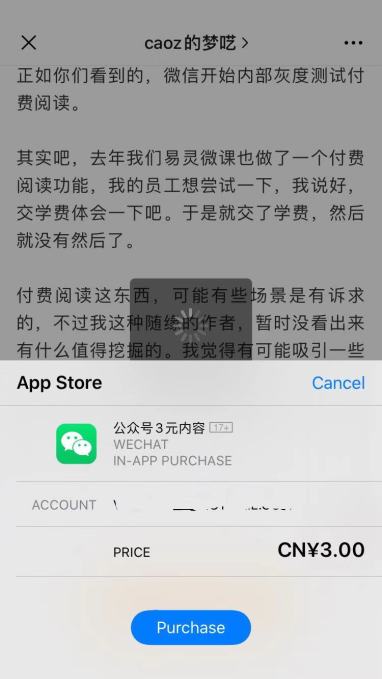
WeChat launched its long-awaited paywall for articles published on its platform
Let’s rewind to 2017 when WeChat, in a much-anticipated move, added a “tipping” feature to articles published on Official Account. The function was meant to boost user engagement and incentivize writers off the back of the popularity of online tipping in China. On live streaming platforms, for instance, users consume content for free but many voluntarily send hosts tips and virtual gifts worth from a few yuan to the hundreds.
WeChat said at the time that all transfers from tipping would go toward the authors, but Apple thought otherwise, claiming that such tips amounted to “in-app purchases” and thus entitled it to a 30% cut from every transaction, or what is widely known as the “Apple tax.”
WeChat disabled tipping following the clash over the terms but reintroduced the feature in 2018 after reaching consensus with Apple. The function has been up and running since then and neither WeChat nor Apple charged from the transfers, a spokesperson from WeChat confirmed with TechCrunch.
If the behemoths’ settlement over tipping was a concession on Apple’s end, Tencent has budged on paywalls this time.
Unlike tipping, the new paywall feature entitles Apple to its standard 30% cut of in-app transactions. That means transfers for paid content will go through Apple’s in-app purchase (IAP) system rather than WeChat’s own payments tool, as is the case with tipping. It also appears that only users with a Chinese Apple account are able to pay for WeChat articles. TechCrunch’s attempt to purchase a post using a U.S. Apple account was rejected by WeChat on account of the transaction “incurring risks or not paying with RMB.”
The launch is certainly a boon to creators who enjoy a substantial following, although many of them have already explored third-party platforms for alternative commercial possibilities beyond the advertising and tipping options that WeChat enables. Zhishi Xingqiu, the “Knowledge Planet”, for instance, is widely used by WeChat creators to charge for value-added services such as providing readers with exclusive industry reports. Xiaoe-tong, or “Smart Little Goose”, is a popular tool for content stars to roll out paid lessons.
Not everyone is bullish on the new paywall. One potential drawback is it will drive down traffic and discourage advertisers. Others voice concerns that the paid feature is vulnerable to exploitation by clickbait creators. On that end, WeChat has restricted the application to the function only to accounts that are over three months old, have published at least three original articles and have seen no serious violations of WeChat rules.
No comments
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.